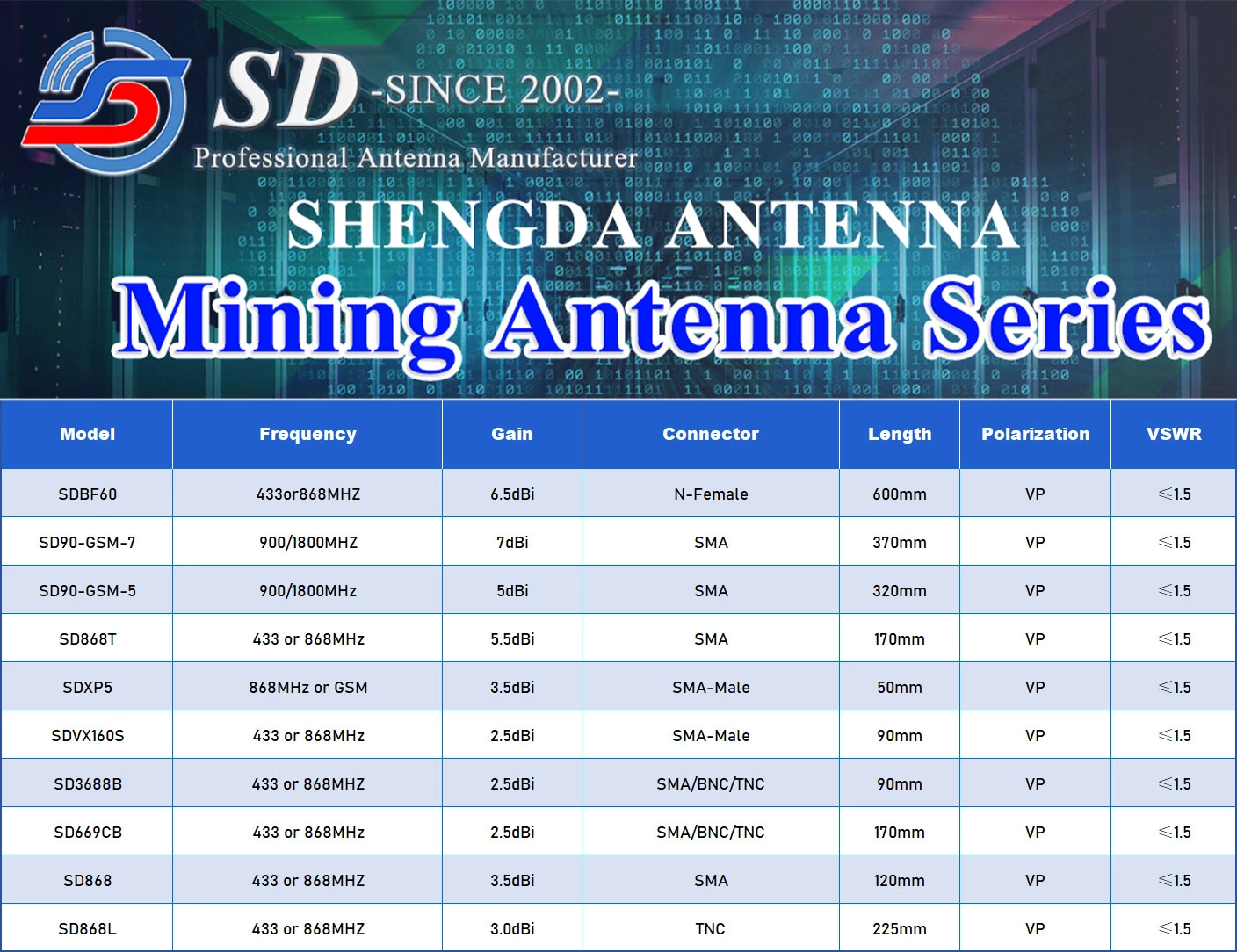
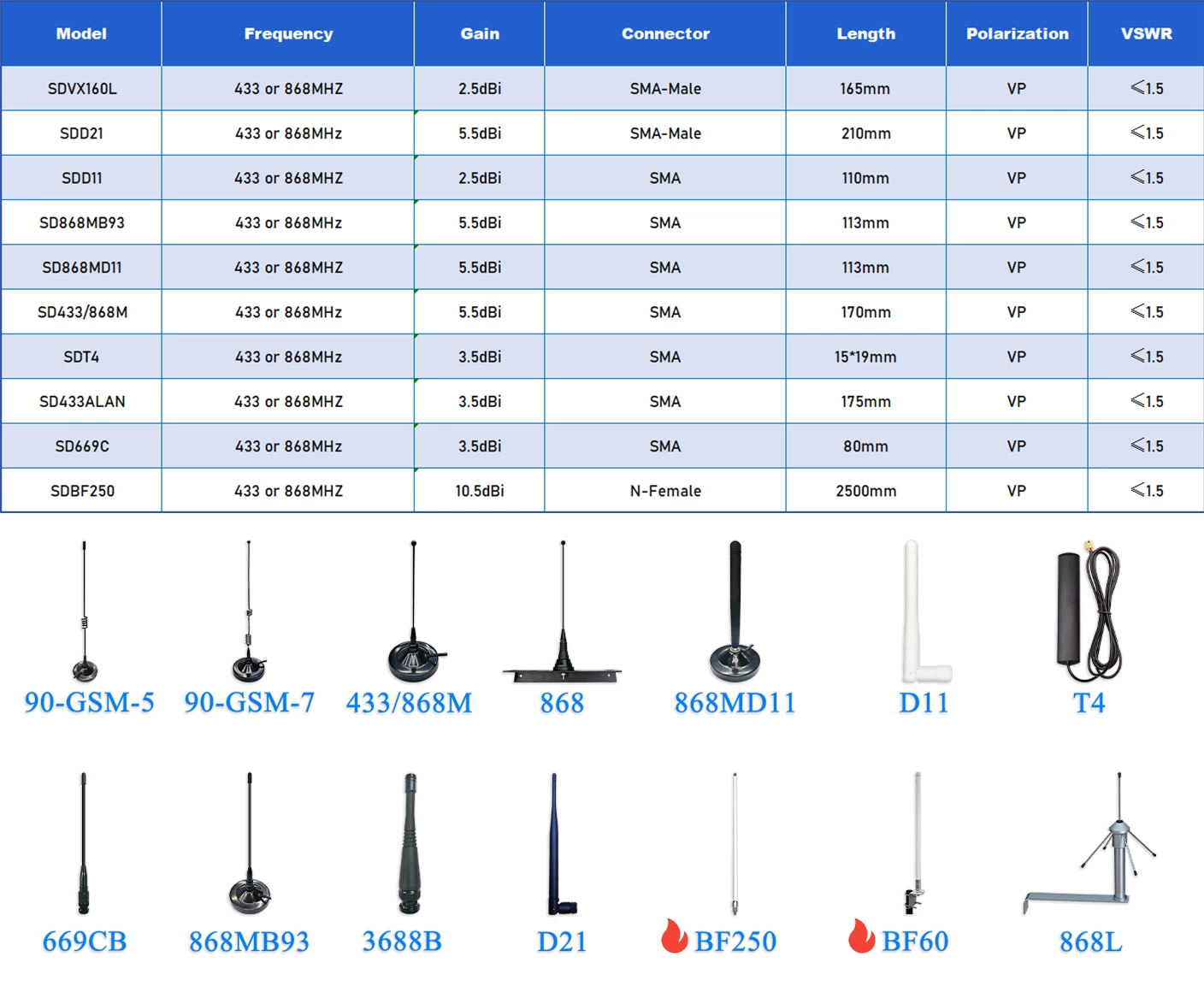
Mining Machine Antennas: The "Signal Hub" of Cryptocurrency Mining and the Key to Enhancing Efficiency
In the cryptocurrency mining industry chain, mining machines serve as the core hash power carriers, and their performance directly determines mining revenue. However, mining machine antennas, which act as the "bridge" for signal transmission, are often overlooked by practitioners.
In fact, the quality, selection, and deployment of mining machine antennas directly affect the communication stability and data transmission efficiency between mining machines and mining pools, and even indirectly determine the effectiveness of hash power output. Inferior or improperly matched antennas may cause signal interruptions, excessive latency, causing mining machines to miss hash power competition opportunities and result in potential revenue loss.
This article will comprehensively analyze mining machine antennas from the aspects of core positioning, core functions, classification characteristics, technical parameters, selection and deployment, common problems, and future trends, providing practical references for mining practitioners.
I. Core Positioning: The "Signal Link" of Mining Machines
Mining machine antennas are key peripheral accessories of mining machines. Their core function is to realize the reception and transmission of wireless signals between mining machines, mining pools, and node networks, undertaking the transmission mission of core data such as hash power data upload, mining task download, and node communication synchronization.
Different from ordinary communication antennas, mining machine antennas need to adapt to the special needs of mining scenarios—such as long-term high-load operation, dense deployment of multiple devices, and possible complex electromagnetic environments (e.g., multi-device interference in mining farms). Therefore, they have more stringent requirements for stability, anti-interference performance, and signal gain.
From the perspective of mining logic, the hash power output of mining machines needs to reach "consensus" with the mining pool through signal transmission. The signal quality of the antenna directly determines the real-time performance and accuracy of data transmission: stable signals result in a high proportion of effective hash power contribution, while signal fluctuations may lead to data packet loss and task synchronization delays, thereby reducing mining revenue.
It can be said that mining machine antennas are the "invisible cornerstone" for the monetization of mining machine hash power, and their performance shortcomings will directly restrict the core efficiency of mining machines.

II. Core Functions: Ensuring Mining Efficiency in Three Dimensions
The value of mining machine antennas is not simply "receiving signals", but comprehensively improving mining efficiency and reducing operational risks from three dimensions: signal enhancement, stability guarantee, and anti-interference protection.
1. Signal Enhancement: Breaking Through Distance and Obstruction Limitations
Mining scenarios are diverse, including centralized mining farms (mostly deployed in suburban areas and factories) and individual small-scale mining nodes (which may be deployed indoors or in remote areas). In some scenarios, mining machines are far away from signal base stations and mining pool servers, or there are obstructions such as walls and metal components, leading to severe signal attenuation.
Through optimized gain design, mining machine antennas can effectively enhance signal strength and extend signal transmission distance. For example, high-gain antennas can focus signal energy to break through obstruction barriers, allowing mining machines in remote areas to stably connect to the mining pool network and avoid hash power idleness caused by weak signals.
2. Stability Guarantee: Reducing Hash Power Loss
Cryptocurrency mining is a 24/7 "hash power competition", and a 1-second signal interruption may cause the loss of mining opportunities. By optimizing impedance matching and signal bandwidth design, mining machine antennas can achieve long-term stable transmission and reduce the probability of signal fluctuations and interruptions.
High-quality mining machine antennas can adapt to the high-frequency data transmission needs of mining machines, avoiding "disconnection" between mining machines and mining pools due to signal latency and packet loss, ensuring continuous and effective hash power output, and maximizing mining revenue.
3. Anti-Interference Protection: Coping with Complex Electromagnetic Environments
In centralized mining farms, hundreds or thousands of mining machines are densely deployed, and each device generates electromagnetic radiation, forming a complex electromagnetic interference environment. At the same time, there may be signal interference from other electronic devices and communication base stations around the mining farm. These interferences will cause distortion of mining machine signals and affect data transmission quality.
Through the use of anti-interference materials and optimized frequency band filtering design, mining machine antennas can effectively shield clutter interference, focus on signals in the core working frequency band, and ensure stable communication quality even in complex environments.

III. Mainstream Classification: "Signal Tools" Adapted to Scenarios
According to application scenarios and technical characteristics, mining machine antennas can be divided into various types. Different types of antennas have significant differences in gain, directionality, and applicable scenarios, and need to be accurately selected according to mining needs.
1. Classification by Directionality: Omnidirectional Antennas vs. Directional Antennas
This is the core classification method of mining machine antennas, which directly determines the signal coverage range and transmission direction.
Omnidirectional Antennas: Signals radiate uniformly in 360° direction with no obvious directionality, and the gain is mostly low to medium (3-8 dBi). The advantage is wide coverage, which can receive signals from multiple directions at the same time, suitable for scenarios with dense deployment of multiple mining machines and scattered signal sources (such as indoor small-scale mining farms and individual mining nodes). The disadvantage is scattered signal energy, limited transmission distance, and fast signal attenuation in long-distance and strong obstruction scenarios. Common types include rubber rod antennas and ceiling-mounted antennas, which are easy to install and low in cost, making them the mainstream choice for individual mining and small-scale mining farms.
Directional Antennas: Signal energy is focused on a specific direction (e.g., 15°-60° beamwidth), and the gain is mostly high (8-18 dBi). In some special scenarios, the antenna gain can reach more than 20 dBi. The advantage is long signal transmission distance and strong anti-interference ability, suitable for scenarios where mining machines are deployed in remote areas with a single signal direction (such as large suburban mining farms that need to point to distant signal base stations or mining pool servers). The disadvantage is narrow coverage, which requires precise adjustment of the installation angle to ensure the signal points to the target direction; otherwise, signal failure will occur. Common types include panel antennas and Yagi antennas, which are slightly more difficult to install but can effectively break through long-distance and obstruction limitations.
2. Classification by Installation Scenario: Indoor Antennas vs. Outdoor Antennas
Indoor Antennas: Suitable for indoor mining scenarios (such as homes and small offices), small in size, easy to install (mostly pole-mounted or desktop-placed), and with moderate protection level (no need for waterproofing and wind resistance). Common types are rubber rod omnidirectional antennas and small ceiling-mounted antennas, with a gain of 3-6 dBi, which can meet short-distance signal transmission needs without interfering with the indoor environment.
Outdoor Antennas: Suitable for outdoor mining farms and remote mining scenarios, need to have waterproof, sunproof, windproof, anti-corrosion and other protection capabilities (protection level is mostly IP65 and above). The gain is mostly high (8-18 dBi), mainly directional antennas (such as panel directional antennas and parabolic antennas), which can cope with complex outdoor environments (such as wind and rain, thunder and lightning, obstructions) and ensure long-term stable operation. Some outdoor antennas also have lightning protection design to reduce the risk of equipment damage caused by severe weather.
3. Classification by Frequency Band: Single-Band Antennas vs. Multi-Band Antennas
The signal transmission of mining machines relies on specific working frequency bands (such as 433MHz, 2.4GHz, 5.8GHz, etc.). Different mining machine models and mining pool communication protocols may correspond to different frequency bands, so the antenna needs to match the corresponding frequency band requirements.
Single-Band Antennas: Only support single frequency band transmission, with high frequency band matching degree and stable signal transmission efficiency, suitable for scenarios with unified mining machine models and fixed communication frequency bands (such as large mining farms with unified deployment of the same model of mining machines). The advantage is strong pertinence and outstanding anti-interference ability; the disadvantage is poor compatibility. If mining machines are replaced or frequency bands are adjusted later, the antenna needs to be replaced simultaneously.
Multi-Band Antennas: Support simultaneous transmission of 2-3 frequency bands (such as 2.4GHz+5.8GHz dual-band), with strong compatibility, and can adapt to the frequency band requirements of various mining machine models and different mining pools, suitable for small-scale mining farms and individual mining (where mining machine models may be replaced). The advantage is high flexibility, no need to frequently replace antennas; the disadvantage is that the gain is slightly lower than that of single-band antennas of the same specification, and the transmission performance in a single frequency band is slightly weaker.
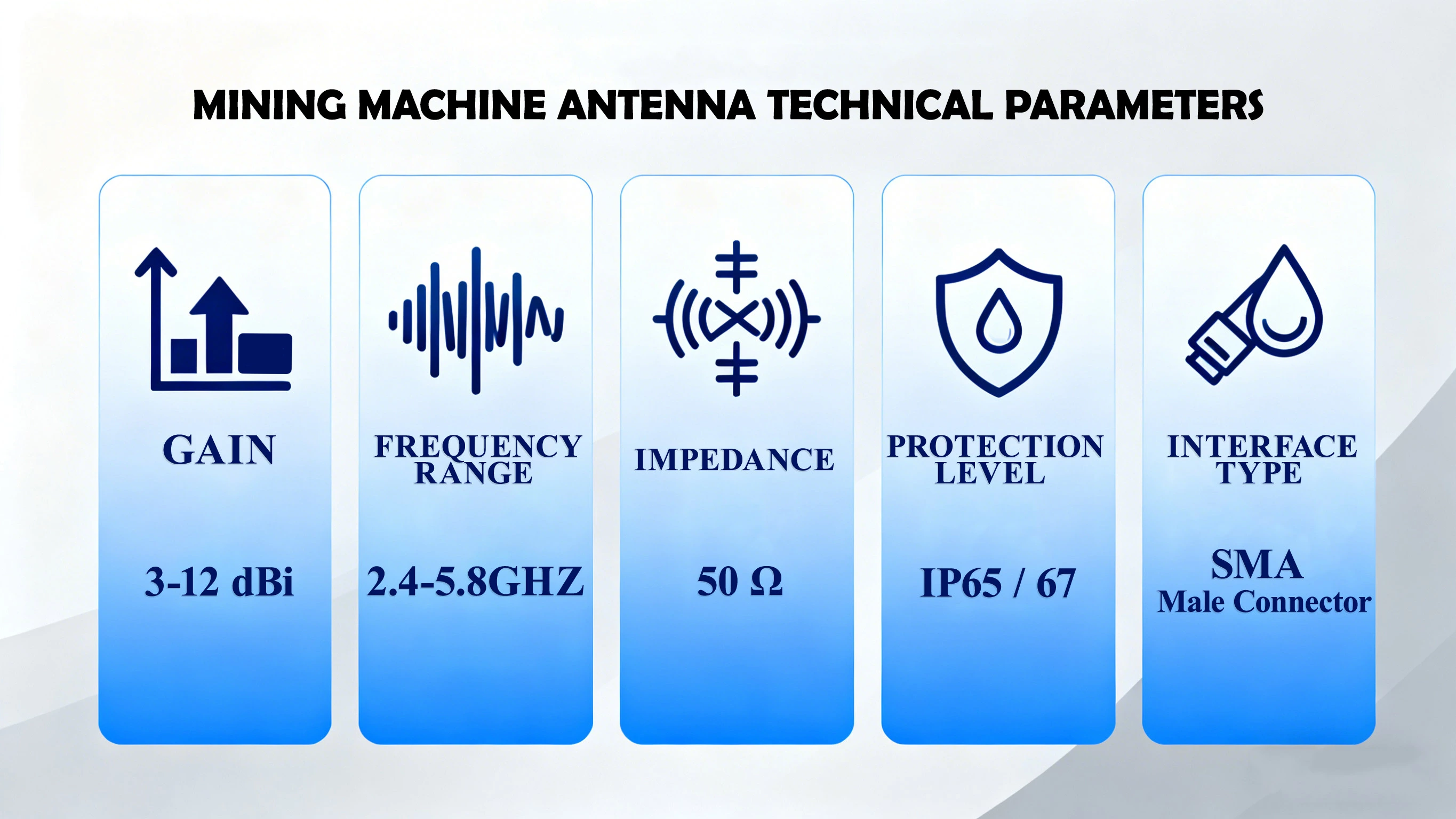
IV. Key Technical Parameters: Core Indicators for Selection
When selecting mining machine antennas, the following core technical parameters should be focused on to avoid performance shortcomings caused by mismatched parameters.
1. Gain (dBi): Determines Signal Transmission Distance and Strength
Gain is the core performance indicator of an antenna, representing the ability of the antenna to focus signal energy, with the unit of dBi. The higher the gain, the longer the signal transmission distance and the stronger the anti-interference ability, but the narrower the signal coverage range (especially for directional antennas).
Selection should be based on deployment distance and obstruction conditions: low-gain antennas (3-6 dBi) can be selected for short-distance and unobstructed scenarios (such as indoors); high-gain antennas (8-18 dBi) can be selected for long-distance and obstructed scenarios (such as outdoor remote mining farms). It should be noted that higher gain is not always better. Excessively high gain will lead to too narrow signal coverage, requiring precise adjustment of the installation angle; otherwise, it will affect signal quality.
2. Frequency Range (MHz/GHz): Ensuring Compatibility with Mining Machines
The frequency range of the antenna must be consistent with the working frequency band of the mining machine and the communication frequency band of the mining pool; otherwise, signal transmission cannot be realized. For example, if the working frequency band of the mining machine is 2.4GHz, selecting an antenna that only supports 5.8GHz will result in signal mismatch, making the mining machine unable to connect to the mining pool.
When selecting, first confirm the frequency band parameters of the mining machine, then select the antenna corresponding to the frequency band; if it is necessary to be compatible with multiple mining machines, a multi-band antenna can be selected.
3. Impedance (Ω): Ensuring Signal Transmission Efficiency
The impedance of the mining machine antenna needs to match the impedance of the radio frequency interface of the mining machine (the impedance of mainstream mining machines is mostly 50Ω). If the impedance is mismatched, it will cause signal reflection and attenuation, reduce data transmission efficiency, and even damage the radio frequency module of the mining machine.
When selecting, confirm that the antenna impedance is consistent with the mining machine to avoid hash power loss and equipment failure caused by impedance mismatch.
4. Protection Level (IP): Adapting to Different Environments
The protection level (such as IP65, IP67) represents the waterproof, dustproof, and anti-corrosion capabilities of the antenna, mainly for outdoor scenarios. Outdoor mining farms need to select antennas with IP65 or above protection level to ensure resistance to wind and rain, dust, ultraviolet radiation, etc.; indoor scenarios have lower requirements for protection level, and IP44 or above can meet the needs.
5. Interface Type: Ensuring Installation Compatibility
The interface of the mining machine antenna needs to match the radio frequency interface of the mining machine. Mainstream interface types include SMA, BNC, N-type, etc., among which the SMA interface (divided into male and female) is a common interface for mining machine antennas. When selecting, confirm the interface model of the mining machine to avoid inability to install due to interface mismatch.
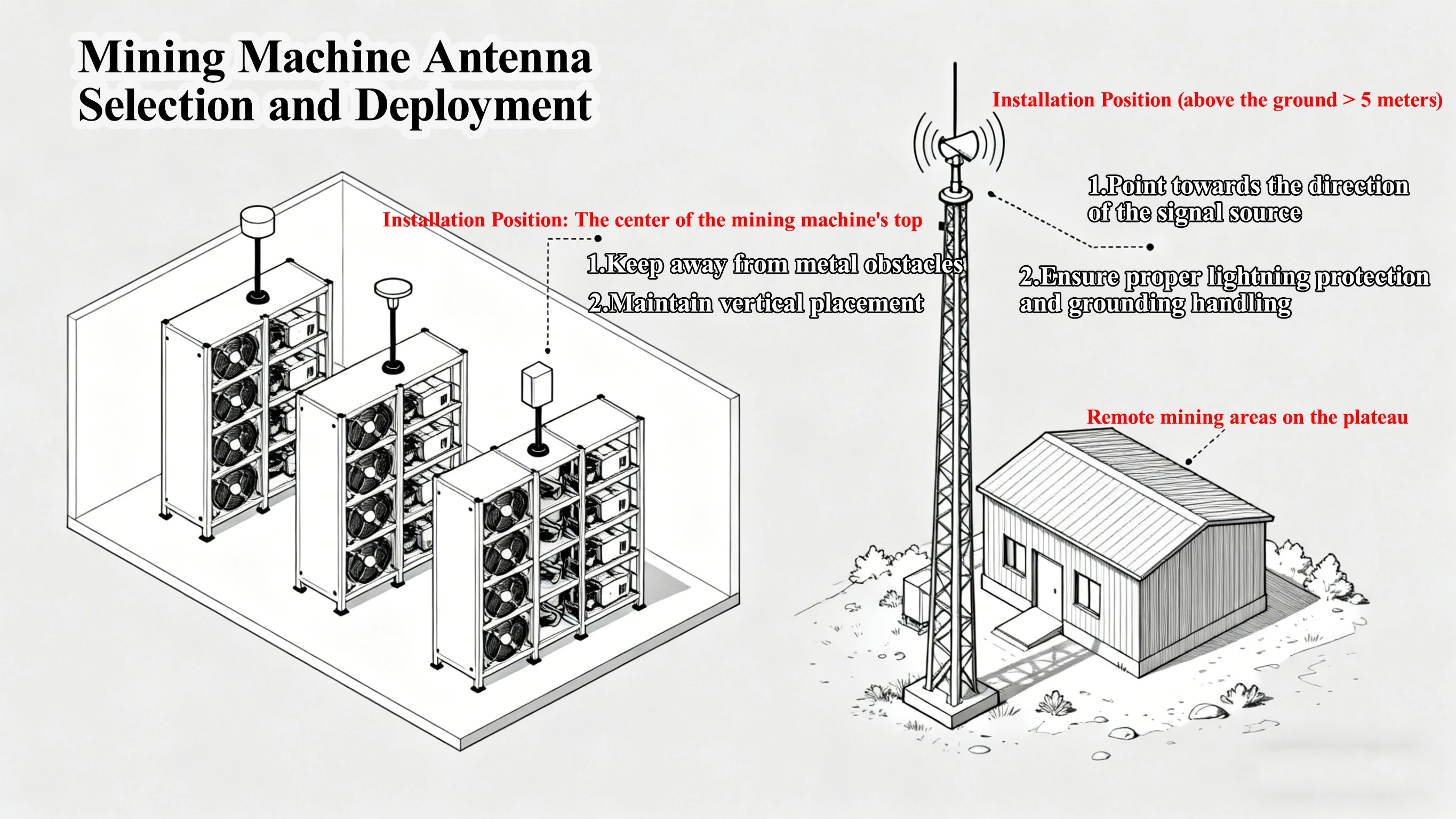
V. Selection and Deployment Skills: Maximizing Antenna Efficiency
High-quality mining machine antennas need to be combined with scientific selection and deployment to give full play to their performance advantages. The following are highly practical selection and deployment skills to help practitioners avoid common mistakes.
1. Selection Skills: Matching on Demand, Rejecting "Blindly Pursuing High Specifications"
Match directionality according to scenarios: select omnidirectional antennas for indoor and dense deployment of multiple mining machines; select directional antennas for outdoor and long-distance transmission, and accurately confirm the signal direction (such as the location of mining pool servers and signal base stations).
Match gain according to distance: for transmission distance < 100 meters and unobstructed, select low-gain antennas (3-6 dBi); for 100 meters - 1 kilometer and slight obstruction, select medium-gain antennas (6-12 dBi); for > 1 kilometer and multiple obstructions, select high-gain antennas (12-18 dBi).
Adapt to mining machine frequency band and interface: prioritize selecting antennas that are fully compatible with the mining machine's frequency band and interface; if mining machines may be replaced later, reserve adaptation space for multi-band antennas.
Balance cost and performance: individual mining and small-scale mining farms can select cost-effective omnidirectional antennas (such as rubber rod antennas); large-scale mining farms and long-distance scenarios need to prioritize performance, selecting high-gain and high-protection-level directional antennas to avoid large-scale hash power loss caused by antenna failures.
2. Deployment Skills: Details Determine Signal Quality
Installation location: avoid interference and obstructions: the antenna should be installed in an unobstructed location far from interference sources (such as high places in outdoor mining farms and window positions indoors), avoiding proximity to metal components and other electronic devices (such as mining machine power supplies and routers) to reduce electromagnetic interference and signal obstruction; directional antennas need to be accurately adjusted in angle to point to the target signal direction (signal strength can be confirmed by a signal detector).
Installation height: improve coverage: the installation height of outdoor antennas is recommended to be more than 3 meters to avoid ground obstruction and interference; indoor antennas can be installed at high wall positions or on the roof to ensure uniform signal coverage of the mining machine deployment area.
Cable selection and layout: the connecting cable between the antenna and the mining machine should be a low-loss coaxial cable (such as RG58, RG8), and the cable length should be as short as possible (excessively long cables will cause signal attenuation); cable layout should avoid sharp objects and high-temperature areas to prevent signal interruption caused by cable damage.
Lightning protection and grounding: ensure outdoor safety: outdoor antennas need to be equipped with lightning protection devices (such as lightning arresters) and properly grounded to avoid damage to antennas and mining machines caused by thunderstorms; the grounding resistance should be controlled below 4Ω to ensure lightning protection effect.
VI. Common Problems and Solutions: Avoiding Mining "Signal Pitfalls"
During mining, antenna-related faults often lead to abnormal signals and decreased hash power. The following are common problems and targeted solutions.
1. Weak Signal and Short Transmission Distance
Causes: Too low antenna gain, obstructed installation location, mismatched frequency band, excessive cable loss.
Solutions: Replace with a high-gain antenna; adjust the installation location to avoid obstructions and interference sources; confirm that the antenna frequency band is consistent with the mining machine; replace with a low-loss coaxial cable and shorten the cable length.
2. Signal Fluctuations and Frequent Interruptions
Causes: Antenna impedance mismatch, severe electromagnetic interference, insufficient protection (outdoor antenna water ingress, aging).
Solutions: Replace with an antenna that matches the mining machine's impedance; adjust the antenna location to stay away from interference sources (such as mining machine power supplies and other electronic devices); check the protection status of outdoor antennas, replace aging and water-injected antennas, and do a good job in waterproof and dustproof treatment.
3. Mining Machine Unable to Connect to Mining Pool
Causes: Antenna frequency band mismatch with mining pool communication frequency band, poor interface contact, antenna failure.
Solutions: Confirm the mining pool communication frequency band and replace with an antenna of the corresponding frequency band; check the interface connection between the antenna and the mining machine to ensure good contact; replace with a spare antenna to check if it is an antenna failure itself.
4. Decreased Hash Power and Reduced Revenue
Causes: Excessively high signal latency, severe data packet loss, insufficient antenna gain leading to low proportion of effective hash power contribution.
Solutions: Replace with a high-gain directional antenna to improve signal transmission real-time performance; optimize the antenna installation location to reduce signal attenuation; check for electromagnetic interference and do a good job in anti-interference protection.
VII. Future Trends: Intelligence and High Efficiency Going Hand in Hand
With the iteration of cryptocurrency mining technology and the large-scale development of mining farms, mining machine antennas are also showing a development trend of intelligence, high efficiency, and integration.
1. Intelligence: Adaptive Adjustment and Remote Monitoring
Future mining machine antennas will integrate intelligent chips to realize adaptive adjustment of signal gain, frequency band, and direction—they can automatically optimize parameters according to the mining farm's electromagnetic environment and signal strength to improve signal stability; at the same time, they support remote monitoring. Practitioners can real-time check the antenna's working status (such as signal strength, temperature, fault warning) through mobile phones and computers to realize remote operation and maintenance and reduce labor costs.
2. High Efficiency: Higher Gain and Lower Loss
In response to the mining needs of long-distance and complex environments, high-gain and low-loss mining machine antennas will become the mainstream. By optimizing the antenna structure design (such as multi-element array, beamforming technology), while improving gain, it reduces signal attenuation and energy consumption, realizing the dual advantages of "long-distance transmission + low-power operation", which is suitable for the efficient mining needs of large-scale mining farms.
3. Integration: Multi-Functional Integrated Design
Future mining machine antennas will integrate multiple functions such as lightning protection, waterproofing, anti-interference, and signal amplification to realize an integrated design—no need to install additional lightning arresters and signal amplifiers, simplifying the deployment process; at the same time, multi-band integrated antennas will be more mature, which can adapt to various mining machine models and communication protocols, improving compatibility and flexibility, and meeting the large-scale and diversified mining needs of mining farms.

VIII. Summary: Small Antennas, a Key Variable for Mining Efficiency
As the "signal hub" of mining equipment, the performance of mining machine antennas directly affects the hash power output and mining revenue of mining machines, and is by no means a dispensable "accessory".
In actual mining scenarios, practitioners need to accurately select antenna types, scientifically plan installation and deployment, and do a good job in daily maintenance in combination with factors such as deployment environment, mining machine model, and transmission distance, so as to give full play to the signal enhancement, stability guarantee, and anti-interference protection functions of the antenna and maximize mining revenue.
With the standardization and technological iteration of the mining industry, mining machine antennas will develop towards intelligence, high efficiency, and integration, becoming an important support for the efficient operation of mining farms. In the future, mining models that ignore the value of antennas will be gradually eliminated. Accurately matched and scientifically deployed antenna configurations will become the key for mining practitioners to improve their core competitiveness.